오늘은 아는 동생이 학교에서 배운 자료구조를 C언어를 통해 만들고 싶다고 하여 작성해보는 시간을 가져보자. 맥에서 C 프로그래밍 하는 방법은 여기를 통해 확인하자!
Stack
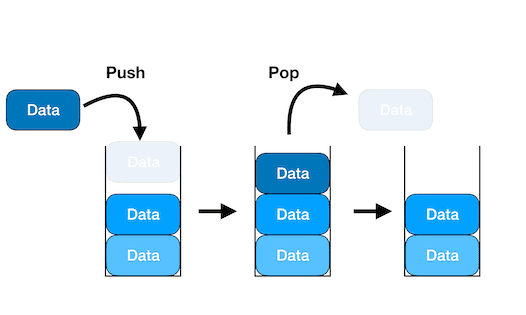
우선 Stack(스택)이 무엇이냐 하면. LIFO(Last-In-First-Out)의 성질을 가지고 있는 자료구조이다. 늦게 들어온 놈이 처음 나간다!
Static Stack - 정적 구조 스택
구조체
간단하게 int형을 기반으로한 Stack 구조체를 생성했다. Stack 구조체는 데이터를 담아두는 배열 int arr[], 인덱스 역할을 하는 int top으로 구성되어 있다.
| #include <stdio.h> | |
| #define MAX_STACK_SIZE 100 | |
| typedef struct { | |
| int arr[MAX_STACK_SIZE]; | |
| int top; | |
| } Stack; |
데이터 초기화
top 데이터는 가장 최신 데이터의 인덱스를 저장해야하며, 처음에는 데이터가 없기 때문에 -1로 초기화 한다.
| void init(Stack *s) { | |
| printf("initialize stack...\n"); | |
| s -> top = -1; | |
| printf("initiallize stack complete!\n"); | |
| } |
상태 체크
스택에 값을 넣거나 빼거나 할때 스택이 꽉 찼는지 비워져있는지 확인해야한다.
| int isEmpty(Stack *s) { | |
| return s -> top == -1; | |
| }; | |
| int isFull(Stack *s) { | |
| return s -> top == (MAX_STACK_SIZE - 1); | |
| }; |
값 추가
우선 스택이 꽉 찼는지 체크하고 괜찮으면 데이터를 arr에 추가하고 top을 +1 한다.
| void push(Stack *s, int value) { | |
| if(isFull(s)) printf("Stack is full..."); | |
| else s->arr[++(s->top)] = value; | |
| }; |
값 제거
스택이 비워져있는지 체크하고 괜찮으면 데이터를 top을 -1 하고 arr에서 데이터를 빼고 그 데이터를 반환한다.
| int pop(Stack *s) { | |
| if(isEmpty(s)) return printf("Stack is empty..."); | |
| else return s->arr[(s->top)--]; | |
| }; |
마지막 값 출력
스택이 비워져있는지 체크하고 괜찮으면 top이 가리키는 arr 요소를 반환한다.
| int peek(Stack *s) { | |
| if(isEmpty(s)) return printf("Stack is empty..."); | |
| else return s->arr[(s->top)]; | |
| }; |
테스트
스택을 s로 선언하고 데이터를 1,2,3,4,5를 순서대로 저장하고 마지막 데이터를 출력, 제거를 반복한다.
| int main() { | |
| Stack s; | |
| init(&s); | |
| push(&s, 1); | |
| push(&s, 2); | |
| push(&s, 3); | |
| push(&s, 4); | |
| push(&s, 5); | |
| printf("Peek: %d\n", peek(&s)); | |
| printf("Pop: %d\n", pop(&s)); | |
| printf("Peek: %d\n", peek(&s)); | |
| printf("Pop: %d\n", pop(&s)); | |
| printf("Peek: %d\n", peek(&s)); | |
| printf("Pop: %d\n", pop(&s)); | |
| printf("Peek %d\n", peek(&s)); | |
| return 0; | |
| }; |
코드
| #include <stdio.h> | |
| #define MAX_STACK_SIZE 100 | |
| typedef struct { | |
| int arr[MAX_STACK_SIZE]; | |
| int top; | |
| } Stack; | |
| void init(Stack *s) { | |
| printf("initialize stack...\n"); | |
| s -> top = -1; | |
| printf("initiallize stack complete!\n"); | |
| } | |
| int isEmpty(Stack *s) { | |
| return s -> top == -1; | |
| }; | |
| int isFull(Stack *s) { | |
| return s -> top == (MAX_STACK_SIZE - 1); | |
| }; | |
| void push(Stack *s, int value) { | |
| if(isFull(s)) printf("Stack is full..."); | |
| else s->arr[++(s->top)] = value; | |
| }; | |
| int pop(Stack *s) { | |
| if(isEmpty(s)) return printf("Stack is empty..."); | |
| else return s->arr[(s->top)--]; | |
| }; | |
| int peek(Stack *s) { | |
| if(isEmpty(s)) return printf("Stack is empty..."); | |
| else return s->arr[(s->top)]; | |
| }; | |
| int main() { | |
| Stack s; | |
| init(&s); | |
| push(&s, 1); | |
| push(&s, 2); | |
| push(&s, 3); | |
| push(&s, 4); | |
| push(&s, 5); | |
| printf("Peek: %d\n", peek(&s)); | |
| printf("Pop: %d\n", pop(&s)); | |
| printf("Peek: %d\n", peek(&s)); | |
| printf("Pop: %d\n", pop(&s)); | |
| printf("Peek: %d\n", peek(&s)); | |
| printf("Pop: %d\n", pop(&s)); | |
| printf("Peek %d\n", peek(&s)); | |
| return 0; | |
| }; |
Dynamic Stack - 동적 구조 스택
정적 구현은 arr을 배열로 선언하고 그 크기를 제한했다. 동적 구현의 경우 arr을 단순한 변수 형태로 동적 메모리를 선언해서 사용한다. 기본적인 구조는 정적 구조 스택과 비슷하므로 변경된 사항만 작성하도록 하겠다. 여기서는 arr을 data로 변경
구조체
| #include <stdio.h> | |
| #include <stdlib.h> | |
| typedef struct { | |
| int *data; | |
| int capacity; | |
| int top; | |
| } Stack; |
배열이 사라지고 capacity, 즉 최대 용량을 뜻하는 변수가 추가되었다.
데이터 초기화
| void init(Stack *s) { | |
| s -> top = -1; | |
| s -> capacity = 1; | |
| s -> data = (int*)malloc(s -> capacity * sizeof(int)); | |
| } |
top은 기존과 같이 -1, capacity는 1, data는 capacity 크기 만큼 동적 메모리를 할당한다.
상태 체크 - isFull
| int isFull(Stack *s) { | |
| return s -> top == (s -> capacity - 1); | |
| }; |
최대 용량인 capacity랑 top이 같을 경우 스택이 꽉 찼다고 설정함.
값 추가
| void push(Stack *s, int value) { | |
| if(isFull(s)) { | |
| s -> capacity *= 2; | |
| s -> data = (int*)realloc(s -> data, s -> capacity * sizeof(int)); | |
| } | |
| s->data[++(s->top)] = value; | |
| } |
동적 구조이므로 스택이 꽉 차면 현재 최대 용량을 2배로 늘리고 data의 정보는 그대로 유지한 체 data의 크기를 늘려준다.
코드
| #include <stdio.h> | |
| #include <stdlib.h> | |
| typedef struct { | |
| int *data; | |
| int capacity; | |
| int top; | |
| } Stack; | |
| void init(Stack *s) { | |
| s -> top = -1; | |
| s -> capacity = 1; | |
| s -> data = (int*)malloc(s -> capacity * sizeof(int)); | |
| } | |
| int isEmpty(Stack *s) { | |
| return s -> top == -1; | |
| }; | |
| int isFull(Stack *s) { | |
| return s -> top == (s -> capacity - 1); | |
| }; | |
| void push(Stack *s, int value) { | |
| if(isFull(s)) { | |
| s -> capacity *= 2; | |
| s -> data = (int*)realloc(s -> data, s -> capacity * sizeof(int)); | |
| } | |
| s->data[++(s->top)] = value; | |
| } | |
| int pop(Stack *s) { | |
| if(isEmpty(s)) return printf("Stack is empty.."); | |
| else return s->data[(s->top)--]; | |
| } | |
| int peek(Stack *s) { | |
| if(isEmpty(s)) return printf("Stack is empty.."); | |
| else return s->data[(s->top)]; | |
| } | |
| int main() { | |
| Stack s; | |
| init(&s); | |
| push(&s, 1); | |
| push(&s, 2); | |
| push(&s, 3); | |
| push(&s, 4); | |
| push(&s, 5); | |
| printf("Peek: %d\n", peek(&s)); | |
| printf("Pop: %d\n", pop(&s)); | |
| printf("Peek: %d\n", peek(&s)); | |
| printf("Pop: %d\n", pop(&s)); | |
| printf("Peek: %d\n", peek(&s)); | |
| printf("Pop: %d\n", pop(&s)); | |
| printf("Peek %d\n", peek(&s)); | |
| return 0; | |
| } |
마치며
오랜만에 대학교 1학년때 배웠던 내용을 다시 복습하는 시간을 가졌다. 옛날로 돌아간거 같고 기분이 좋았다. 그때 배웠던 내용을 다시한번 되세기는 시간을 가져야겠다.